

Critical Temperature
Gases can be converted to liquids by compressing the gas at a suitable temperature.
Gases become more difficult to liquefy as the temperature increases because the kinetic energies of the particles that make up the gas also increase.
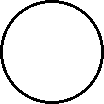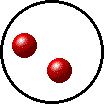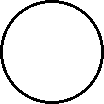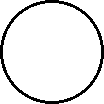 |
 |
| Microscopic view of a gas. | Microscopic view of a liquid. |
The critical temperature of a substance is the temperature at and above which vapor of the substance cannot be liquefied, no matter how much pressure is applied.
Every substance has a critical temperature. Some examples are shown below.
| substance | critical temperature (oC) |
| NH3 | 132 |
| O2 | -119 |
| CO2 | 31.2 |
| H2O | 374 |
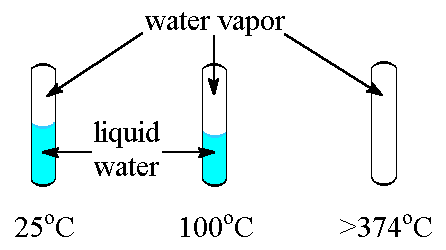 |
| Tubes containing water at several temperatures. Note that at or above 374oC (the critical temperature for water), only water vapor exists in the tube. |
| substance | critical pressure (atm) |
| NH3 | 111.5 |
| O2 | 49.7 |
| CO2 | 73.0 |
| H2O | 217.7 |
