Sabre Kais Group
Quantum Information and Quantum Computation
Measuring Quantum Entanglement in Chemical Reactions
The Einstein, Podolsky, and Rosen (EPR) entanglement, which features the essential difference between classical and quantum physics, has received wide theoretical and experimental attentions. Recently, the desire to understand and create quantum entanglement between particles such as spins, photons, atoms, and molecules is fueled by the development of quantum teleportation, quantum communication, quantum cryptography, and quantum computation.
Although most of the work has focused on showing that entanglement violates the famous Bell’s inequality and its
generalization for discrete measurements, few recent attempts focus on continuous measurement results. Here, we
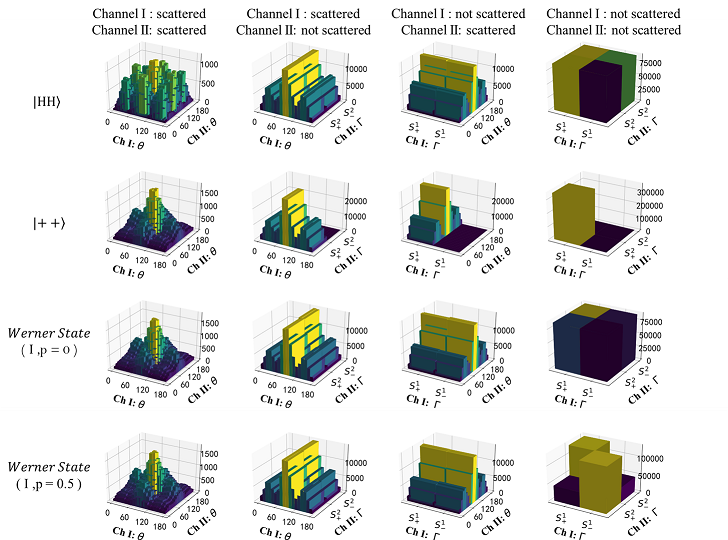
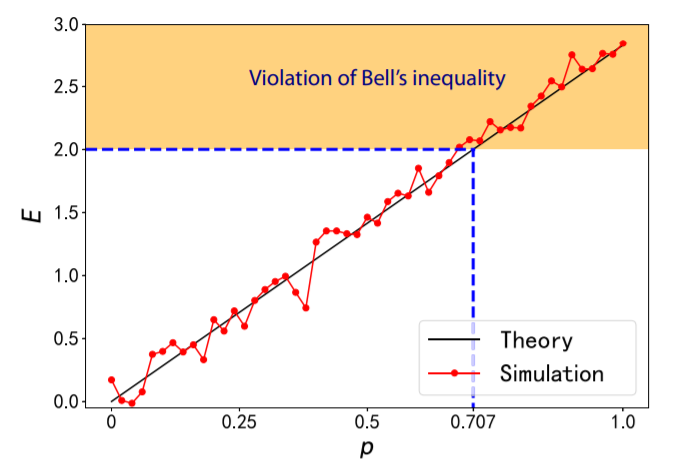
have developed a general practical inequality to test entanglement for continuous measurement results, particularly
scattering of chemical reactions. After we explain how to implement this inequality to classify entanglement in
scattering experiments, we propose a specific chemical reaction to test the violation of this inequality. The method
is general and could be used to classify entanglement for continuous measurement results.
“Entanglement Classifier in Chemical Reactions” by Junxu Li and Sabre Kais, Science, Advances 5: 5283 (2019) pdf