

Bidentate ligands are Lewis bases that donate two pairs ("bi") of electrons to a metal atom.
Bidentate ligands are often referred to as chelating ligands ("chelate" is derived from the Greek word for "claw") because they can "grab" a metal atom in two places.
A complex that contains a chelating ligand is called a chelate.
| Some Bidentate Ligands | |
|---|---|
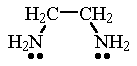 | 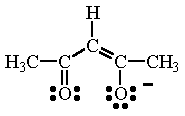 |
| ethylenediammine (en) | acetylacetonate ion (acac) |
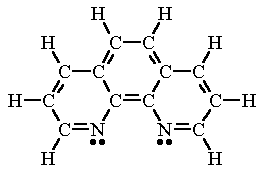 | 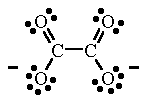 |
| phenanthroline (phen) | oxalate ion (ox) |
|
|
||
| ethylenediammine (en) Ethylenediammine is a neutral molecule containing two N atoms that can each donate a pair of electrons to a metal atom. | Ni(en)2Cl2 In this complex, two ethylenediammine molecules are bonded to the Ni atom. The coordination number of 6 results in an octahedral structure. |
|
| ||
| oxalate ion (ox) Oxalate ion is a bidentate ligand even though it contains four O atoms which have lone pairs of electrons. | [Ni(ox)2]2- In this complex, two oxalate ions are bonded to the Ni atom. The coordination number of 4 results in a square planar structure. |
|
|
||
| phenanthroline (phen) Phenanthroline is a neutral molecule containing two N atoms that can each donate a pair of electrons to a metal atom. | [Rh(phen)2Cl2]+ In this complex, two phenanthroline molecules are bonded to the Rh atom. The coordination number of 6 results in an octahedral structure. |
|
|
||
| acetylacetonate ion (acac) Acetylacetonate ion contains two O atoms which allow this ligand to function as a bidentate ligand. | Cr(acac)3 In this complex, three acetylacetonate ions are bonded to the Cr atom. The coordination number of 6 results in an octahedral structure. |
|
|
||
| oxalate ion (ox) Oxalate ion is a bidentate ligand even though it contains four O atoms which have lone pairs of electrons. |
[Fe(C2O4)3]3- In this complex, three oxalate ions are bonded to the Fe atom. The coordination number of 6 results in an octahedral structure. |
