
Calculating K for a Reaction
Using Known K's for Other Reactions
- K for a Reversed Reaction
- Reaction Coefficients Multiplied by a Number
- Adding Two or More Equations
- Calculations Incorporating Two or More of These Algebraic Manipulations
The equilibrium expression written for a reaction written in the reverse direction is the reciprocal of the one for the forward reaction.
K' is the constant for the reverse reaction and K is that of the forward reaction.
Example: What is the value of the equilibrium constant
for the reaction 2 NO2(g) ![]() N2O4(g)
at 100o C?
N2O4(g)
at 100o C?
N2O4(g) ![]() 2 NO2(g) Kc =
0.212 @ 100oC?
2 NO2(g) Kc =
0.212 @ 100oC?
The desired reaction is the reverse of the reaction for which the Kc is known. The equilibrium expression is the reciprocal of that given.
K'c = 1/Kc = 1/0.212 = 4.72
Reaction Coefficients Multiplied by a Number
If the coefficients in a balanced equation are multiplied by a factor, n, the equilibrium expression is raised to the nth power.
K' is the constant for the reaction multiplied by n and K is the constant of the original reaction.
Example: What is the value of the equilibrium constant
for the reaction, 2 I2(g) + 2 Cl2(g) ![]() 4
ICl(g)?
4
ICl(g)?
� I2(g) + � Cl2 (g) ![]() ICl(g)
Kc = 4.54 x 102 @ 25oC?
ICl(g)
Kc = 4.54 x 102 @ 25oC?
The desired reaction has been multiplied by 4. The value of the equilibrium constant will be the 4th power of the given Kc.
K'c = Kc4 = (4.54 x 102)4 = 4.25 x 1010
If two or more reactions are added to give another, the equilibrium constant for the reaction is the product of the equilibrium constants of the equations added.
K' = K1 x K2 . . .
K1 , K2, etc. represent the equilibrium constants for reactions being added together, and K' represents the equilibrium constant for the desired reaction.
Example: Calculate the value of Kc for the reaction:
2 NO(g) + Br2(g) ![]() 2 NOBr (g) using the following information.
2 NOBr (g) using the following information.
N2(g) + Br2(g) + O2(g)
The two equations can be added to yield the desired equation. The value of Kc for the reaction will be the product of the other two.
K'c = Kc1 x Kc2 = (1 x 1030)(1 x 10-27) = 2 x 103
Calculations Incorporating Two or More of These Algebraic Manipulations
It is possible to combine more than one of these manipulations.
Example: Calculate the value of Kc for
the reaction: 2 N2O(g) + 3 O2(g) ![]() 2 N2O4(g),
using the following information.
2 N2O4(g),
using the following information.
| Equation | Equilibrium Constant |
| 2 N2 (g) + O2(g) |
Kc = 1.2 x 10-35 |
| N2O4(g) |
Kc = 4.6 x 10-3 |
| � N2(g) + O2(g) |
Kc = 4.1 x 10-9 |
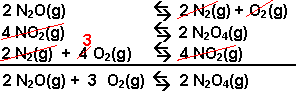
- Write the first equation backwards. The K for this reaction will be the recipricol of the forward reaction.
|
|
|
8.3 x 1034 |
- Write the second equation backwards and multiply the coefficients by 2. The K for this reaction will be the recipricol of the forward reaction squared.
|
|
|
4.7 x 104 |
- Use the third equation in the forward direction but multiplied by 4. The K for this reaction will be the K of the given reaction raised to the fourth power.
|
|
|
2.8 x 10-34 |
- Check to see that the three equations yield the desired equation when added together. The equilibrium constant for the desired equation will be the product of the constants for the three equations combined.
