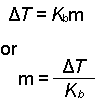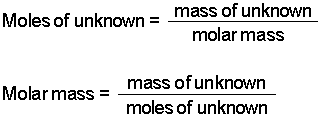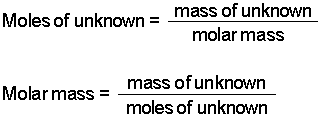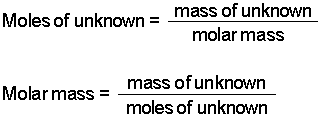Determining
Molar Mass
We can use a measurement of any one of the following properties to
determine the molar mass (molecular weight) of an unknown that is the solute
in a solution:
From Boiling
Point Elevation
- Determine the change in boiling point from the observed boiling
point of the solution and the boiling point of the pure solvent.
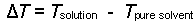
- Determine the molal concentration, m, from the change in boiling
point and the boiling point elevation constant.
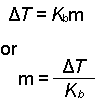
- Determine the moles of unknown (the solute) from the molality
of the solution and the mass of solvent (in kilograms) used to make the
solution.


- Determine the molar mass from the mass of the unknown and the
number of moles of unknown.
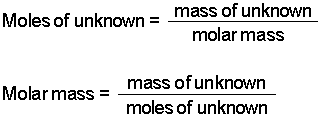
Top
From
Freezing Point Depression
- Determine the change in freezing point from the observed freezing
point of the solution and the freezing point of the pure solvent. (This will be a negative number.)
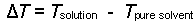
- Determine the molal concentration, m, from the change in freezing
point and the freezing point depression constant.
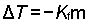
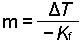
- Determine the moles of unknown (the solute) from the molality
of the solution and the mass of solvent (in kilograms) used to make the
solution.


- Determine the molar mass from the mass of the unknown and the
number of moles of unknown.
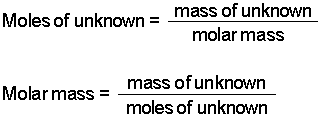
Top
From
Osmotic Pressure
- Determine the molar concentration of the unknown in the solution
from the observed osmotic pressure.
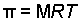
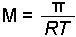
- Determine the moles of unknown (the solute) from the molarity
of the solution and the volume (in liters) of the solution.

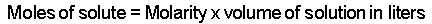
- Determine the molar mass from the mass of the unknown and the
number of moles of unknown.
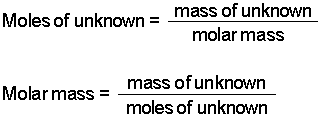
Top