

Dipole-dipole forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule. Dipole-dipole forces have strengths that range from 5 kJ to 20 kJ per mole. They are much weaker than ionic or covalent bonds and have a significant effect only when the molecules involved are close together (touching or almost touching).
The figures show two arrangements of polar iodine monochloride (ICl) molecules that give rise to dipole-dipole attractions.
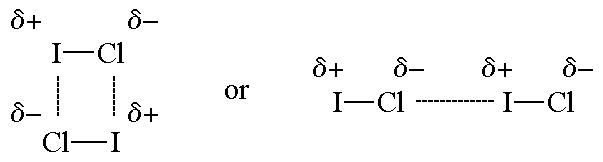
Note:
A dashed line is used to represent an intermolecular attraction between molecules because these forces are NOT as strong as chemical bonds.
|
|
||
| One arrangement of ICl molecules that gives rise to a dipole-dipole attraction. | Another arrangement of ICl molecules that gives rise to a dipole-dipole attraction. |
![]() Click here to check
your answer.
Click here to check
your answer.
