Welcome to the Shah Laboratory
Drug Discovery in Cancer and Alzheimer's Disease Using Chemical Biology
Cdk5 and Nuclear Fragmentation in AD
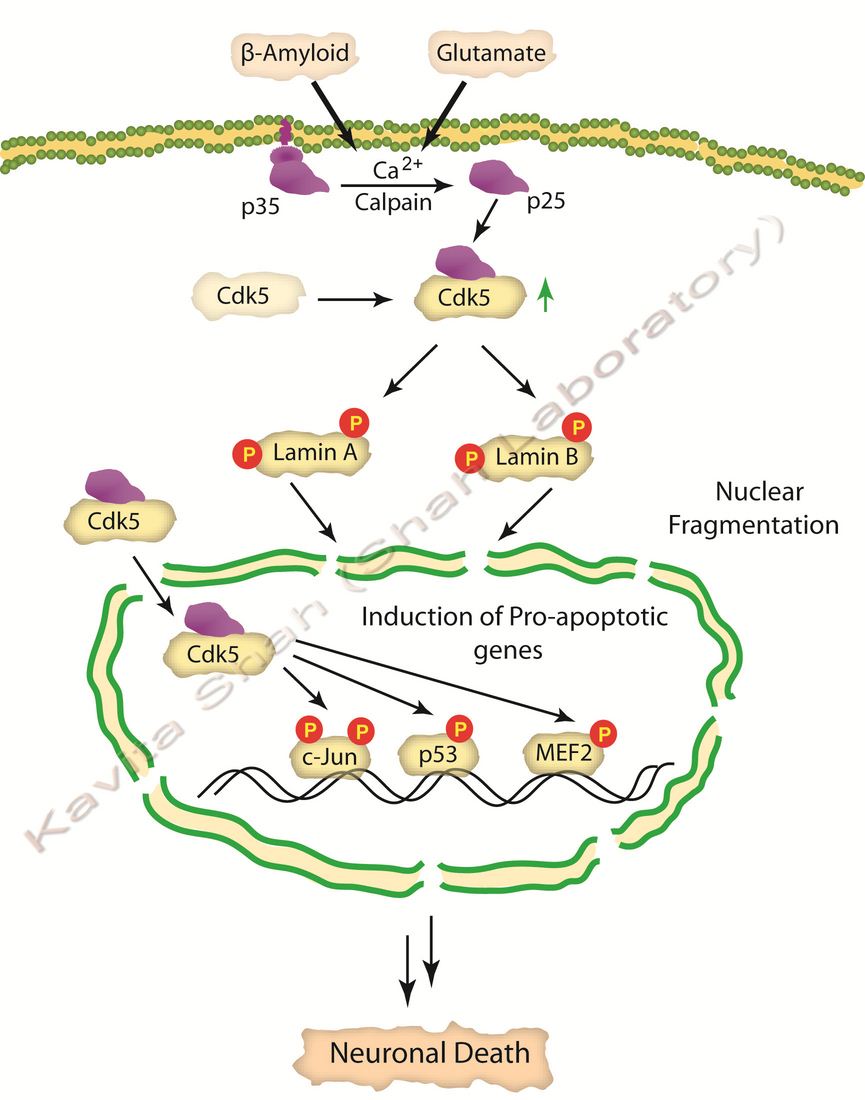
Cdk5 is considered to be neuroprotective in the cytoplasm, and neurotoxic in the nucleus. Our studies have demonstrated that b-amyloid treatment or excitotoxicity deregulates Cdk5 in primary cortical neurons, which phosphorylates nuclear proteins Lamin A and Lamin B1 proteins causing rapid nuclear dispersion. Nuclear dispersion allows Cdk5 to mislocalize in the nucleus, where it triggers the activation of several pro-apoptotic genes leading to neurodegeneration.